OhmAlloy-5J1580(Bimetallic strip)
(Common Name: Kanthal 155)
Bimetallic strip is used to convert a temperature change into mechanical displacement. The strip consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates as they are heated, usually steel and copper, or in some cases steel and brass. The strips are joined together throughout their length by riveting, brazing or welding. The different expansions force the flat strip to bend one way if heated, and in the opposite direction if cooled below its initial temperature. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion is on the outer side of the curve when the strip is heated and on the inner side when cooled.
The sideways displacement of the strip is much larger than the small lengthways expansion in either of the two metals. This effect is used in a range of mechanical and electrical devices. In some applications the bimetal strip is used in the flat form. In others, it is wrapped into a coil for compactness. The greater length of the coiled version gives improved sensitivity.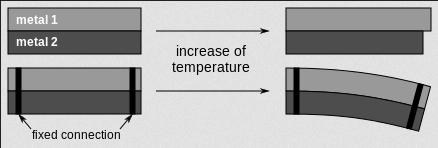
Diagram of a bimetallic strip showing how the difference in thermal expansion in the two metals leads to a much larger sideways displacement of the strip.
Composition
Grade | 5J1580 |
High expansion layer | Ni20Mn6 |
Low expansion layer | Ni36 |
Chemical composition(%)
Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Fe |
Ni36 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.6 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 35~37 | - | - | Bal. |
Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Fe |
Ni20Mn6 | ≤0.05 | 0.15~0.3 | 5.5~6.5 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 19~21 | - | - | Bal. |
Typical Physical properties
Density (g/cm3) | 8.1 |
Electrical resistivity at 20℃(Ωmm2/m) | 0.8±5% |
Thermal conductivity, λ/ W/(m*℃) | 12 |
Elastic Modulus, E/ Gpa | 147~177 |
Bending K / 10-6℃-1(20~135℃) | 15 |
Temperature bending rate F/(20~130℃)10-6℃-1 | 28.5%±5% |
Allowable temperature (℃) | -70~ 350 |
Linear temperature (℃) | -20~ 180 |
Style of supply
Alloys Name | Type | Dimension | |
OhmAlloy-5J1580 | Strip | W= 5~120mm | T= 0.1mm |
Application: The material is mainly in automatic control devices and instrumentation (eg: exhaust thermometers, thermostats, voltage regulators, temperature relay, automatic protection switching, diaphragm meters, etc.) make temperature control, temperature compensation, current limit, temperature indicator and other heat-sensitive components.
Feature: The basic characteristics of Thermostat Bimetallicis bending deformation with temperature changes, resulting in a certain moment.
Thermostat Bimetallic Strip expansion coefficientis different from the two or more layer sofmetalor alloy along the entire contact surface firmly bonded, having atemperature-dependentshape change occurs thermo sensitive functional composites. Where in the higher expansion coefficien to fthe active layer isa layer called alow coefficient of expansion of the layer is namedpassive layer.
OhmAlloy-5J1580(Bimetallic strip)
(Common Name: Kanthal 155)
Bimetallic strip is used to convert a temperature change into mechanical displacement. The strip consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates as they are heated, usually steel and copper, or in some cases steel and brass. The strips are joined together throughout their length by riveting, brazing or welding. The different expansions force the flat strip to bend one way if heated, and in the opposite direction if cooled below its initial temperature. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion is on the outer side of the curve when the strip is heated and on the inner side when cooled.
The sideways displacement of the strip is much larger than the small lengthways expansion in either of the two metals. This effect is used in a range of mechanical and electrical devices. In some applications the bimetal strip is used in the flat form. In others, it is wrapped into a coil for compactness. The greater length of the coiled version gives improved sensitivity.
Diagram of a bimetallic strip showing how the difference in thermal expansion in the two metals leads to a much larger sideways displacement of the strip.
Composition
Grade | 5J1580 |
High expansion layer | Ni20Mn6 |
Low expansion layer | Ni36 |
Chemical composition(%)
Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Fe |
Ni36 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.6 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 35~37 | - | - | Bal. |
Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Fe |
Ni20Mn6 | ≤0.05 | 0.15~0.3 | 5.5~6.5 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 19~21 | - | - | Bal. |
Typical Physical properties
Density (g/cm3) | 8.1 |
Electrical resistivity at 20℃(Ωmm2/m) | 0.8±5% |
Thermal conductivity, λ/ W/(m*℃) | 12 |
Elastic Modulus, E/ Gpa | 147~177 |
Bending K / 10-6℃-1(20~135℃) | 15 |
Temperature bending rate F/(20~130℃)10-6℃-1 | 28.5%±5% |
Allowable temperature (℃) | -70~ 350 |
Linear temperature (℃) | -20~ 180 |
Style of supply
Alloys Name | Type | Dimension | |
OhmAlloy-5J1580 | Strip | W= 5~120mm | T= 0.1mm |
Application: The material is mainly in automatic control devices and instrumentation (eg: exhaust thermometers, thermostats, voltage regulators, temperature relay, automatic protection switching, diaphragm meters, etc.) make temperature control, temperature compensation, current limit, temperature indicator and other heat-sensitive components.
Feature: The basic characteristics of Thermostat Bimetallicis bending deformation with temperature changes, resulting in a certain moment.
Thermostat Bimetallic Strip expansion coefficientis different from the two or more layer sofmetalor alloy along the entire contact surface firmly bonded, having atemperature-dependentshape change occurs thermo sensitive functional composites. Where in the higher expansion coefficien to fthe active layer isa layer called alow coefficient of expansion of the layer is namedpassive layer.